The amount of changed files …

https://github.com/ankitects/anki/commit/5004cd332bf1514e57f5c48bcbe43cd86f982a7a
The amount of changed files …

https://github.com/ankitects/anki/commit/5004cd332bf1514e57f5c48bcbe43cd86f982a7a
Just a discrepancy of review dates that I noticed, still not able to reproduce and report a bug.
There is a known bug that has to do with reviewing cards during the rollover hour (set at 4 hours past midnight as default) but it seems it is not the case here…
https://github.com/ankitects/anki/issues/2606

The problem:

The solution:
sudo rm /var/lib/pacman/db.lck removes the lock of the package database that pacman created when a package is about to get altered. This mechanism prevents a different instance of pacman to perform simultaneous changes but the lock can sometimes remain stale

More about pacman troubleshooting: https://wiki.archlinux.org/title/Pacman#Troubleshooting
According to the 2023’s Second Quarter Status Report boot optimizations speed up kernel boot process.
The developer Colin Percival implemented a mergesort algorithm instead of the 30+ year old bubblesort of SYSINITs.
Bubblesort is a sorting algortithm that compares each element of an array with the next one and sorts them, whereas mergesort divides the array into subarrays. This system boosted speed by a factor of 100x.
https://www.freebsd.org/status/report-2023-04-2023-06/#_boot_performance_improvements
https://cgit.freebsd.org/src/commit/?id=9a7add6d01f3c5f7eba811e794cf860d2bce131d
https://www.theregister.com/2023/08/29/freebsd_boots_in_25ms/
For a detailed changelog see the link below
Η καταληκτική ημερομηνία είναι εντός Φεβρουαρίου 2024
Alpha/freeze θα είναι διαθέσιμη τον Νοέμβριο ενώ Beta, RCs τον Δεκέμβριο

One of them is associated with the update process of the freebsd-update tool, as it incorrectly deleted files in /etc/, in case that the file to be
updated matched the new release and was different than the old release …
Yeap sounds pretty … serious 🙂 Funny is that in order to apply the patch you have to use the same freebsd-update command lol
https://www.freebsd.org/security/advisories/FreeBSD-EN-23:09.freebsd-update.asc
With this commit in Github the version system of Anki adopts a new year.month.patch approach. That means that the current version is 23.09. Damien decided this time period as this version brings some major features including FSRS and Image Occlusion


https://github.com/ankitects/anki/commit/ffd392de211d8c107b1927c6755d103b34bbae23
“A chroot is an operation that changes the apparent root directory for the current running process and their children. A program that is run in such a modified environment cannot access files and commands outside that environmental directory tree. This modified environment is called a chroot jail.”
I always have a spare USB device with an Arch Linux bootable iso just in case my system does not boot or after a package update that totally breaks my system.
In August 2022 there was a major GRUB bug that caused many systems failing to boot. At that time I was not in a home setting so chroot from a USB literally saved me.

Another case was using ibt=off in /etc/default/grub that turns off the Indirect Branch Tracking security feature, after a bug affected Nvidia drivers.
https://github.com/NVIDIA/open-gpu-kernel-modules/issues/256
With Gnome 44 and Plasma KDE 5.27 LTS with KDE Gear 23.08
https://forum.manjaro.org/t/manjaro-23-0-uranos-released/147448
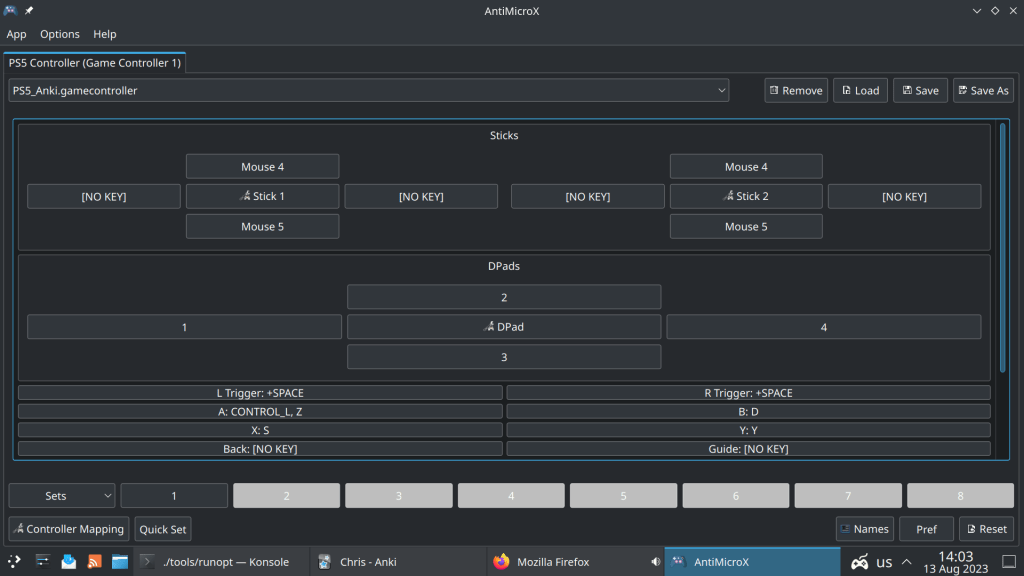
Using Anki at the beginning can be pretty unconfortable, as pressing the spacebar and 1,2,3,4 keys a million times can lead to tendonitis and makes reviews not enjoyable 😦
Instead using a PS4, Xbox or PS4 game controller gives a gaming character to your daily reviews, is easy and can be used while connecting your Laptop with an Ultra HDTV
Installing AntiMicroX, a graphical program used to map gamepad keys to keyboard, mouse, scripts and macros in Arch Linux Distros:
> yay -Ss antimicrox
aur/antimicrox-git 3.3.3.r2.g7a39dc43-1 (+4 0.05)
Map keyboard and mouse actions to gamepad buttons, inspired by qjoypad.
Antimicro fork
aur/antimicrox 3.3.4-1 (+115 0.26) (Installed)
Graphical program used to map keyboard buttons and mouse controls to a
gamepad
antimicrox is the stable release while antimicrox-git is the cutting edge, with the latest commits version.
2 of the most common commands that I use all the time is sudo pacman -Syu for updating packages and sudo pacman -Scc for clearing the package cache
Setting aliases saves a lot of time 🙂
#Aliases
alias update="sudo pacman -Syu && yay -Syu"
alias clearcache="sudo pacman -Scc && yay -Scc"
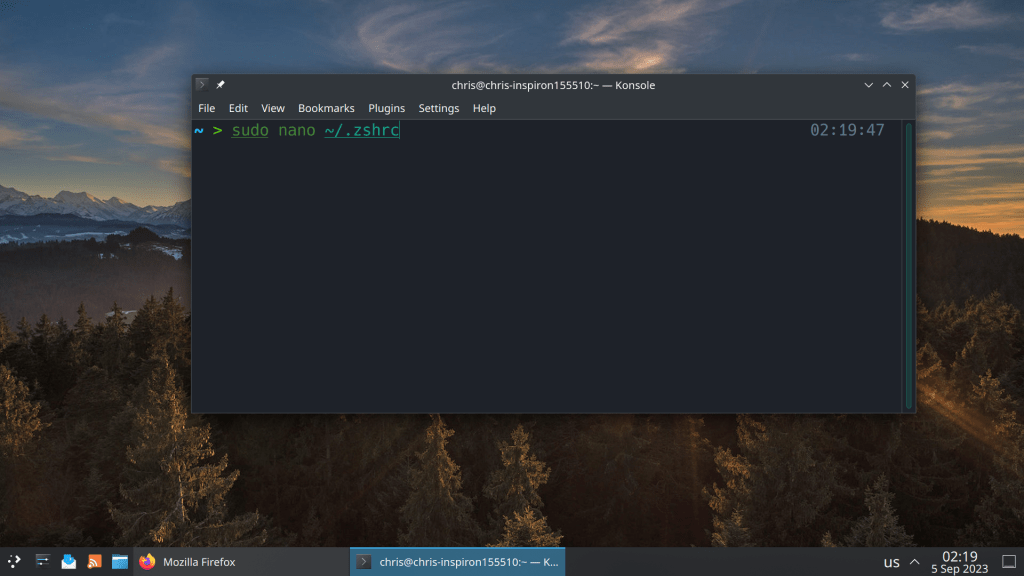
# Enable Powerlevel10k instant prompt. Should stay close to the top of ~/.zshrc.
# Initialization code that may require console input (password prompts, [y/n]
# confirmations, etc.) must go above this block; everything else may go below.
if [[ -r "${XDG_CACHE_HOME:-$HOME/.cache}/p10k-instant-prompt-${(%):-%n}.zsh" ]]; then
source "${XDG_CACHE_HOME:-$HOME/.cache}/p10k-instant-prompt-${(%):-%n}.zsh"
fi
# Use powerline
USE_POWERLINE="true"
# Source manjaro-zsh-configuration
if [[ -e /usr/share/zsh/manjaro-zsh-config ]]; then
source /usr/share/zsh/manjaro-zsh-config
fi
# Use manjaro zsh prompt
if [[ -e /usr/share/zsh/manjaro-zsh-prompt ]]; then
source /usr/share/zsh/manjaro-zsh-prompt
fi
# To customize prompt, run `p10k configure` or edit ~/.p10k.zsh.
[[ ! -f ~/.p10k.zsh ]] || source ~/.p10k.zsh
#Aliases
alias update="sudo pacman -Syu && yay -Syu"
alias clearcache="sudo pacman -Scc && yay -Scc"
Pacman is the default package manager of Arch Linux and Arch Linux based distributions. It is considered as the most robust binary package manager along with Portage of Gentoo, a powerful source code package manager.
One of the most important modifications of my setup is the number of parallel downloads and kde-unstable repository
#
# /etc/pacman.conf
#
# See the pacman.conf(5) manpage for option and repository directives
#
# GENERAL OPTIONS
#
[options]
# The following paths are commented out with their default values listed.
# If you wish to use different paths, uncomment and update the paths.
#RootDir = /
#DBPath = /var/lib/pacman/
CacheDir = /var/cache/pacman/pkg/
#LogFile = /var/log/pacman.log
#GPGDir = /etc/pacman.d/gnupg/
#HookDir = /etc/pacman.d/hooks/
HoldPkg = pacman glibc manjaro-system
# If upgrades are available for these packages they will be asked for first
SyncFirst = manjaro-system archlinux-keyring manjaro-keyring
#XferCommand = /usr/bin/curl -L -C - -f -o %o %u
#XferCommand = /usr/bin/wget --passive-ftp -c -O %o %u
#CleanMethod = KeepInstalled
#UseDelta = 0.7
Architecture = auto
# Pacman won't upgrade packages listed in IgnorePkg and members of IgnoreGroup
#IgnorePkg =
#IgnoreGroup =
#NoUpgrade =
#NoExtract =
# Misc options
#UseSyslog
Color
#NoProgressBar
# We cannot check disk space from within a chroot environment
CheckSpace
VerbosePkgLists
ParallelDownloads = 5
# By default, pacman accepts packages signed by keys that its local keyring
# trusts (see pacman-key and its man page), as well as unsigned packages.
SigLevel = Required DatabaseOptional
LocalFileSigLevel = Optional
#RemoteFileSigLevel = Required
# NOTE: You must run `pacman-key --init` before first using pacman; the local
# keyring can then be populated with the keys of all official Manjaro Linux
# packagers with `pacman-key --populate archlinux manjaro`.
#
# REPOSITORIES
# - can be defined here or included from another file
# - pacman will search repositories in the order defined here
# - local/custom mirrors can be added here or in separate files
# - repositories listed first will take precedence when packages
# have identical names, regardless of version number
# - URLs will have $repo replaced by the name of the current repo
# - URLs will have $arch replaced by the name of the architecture
#
# Repository entries are of the format:
# [repo-name]
# Server = ServerName
# Include = IncludePath
#
# The header [repo-name] is crucial - it must be present and
# uncommented to enable the repo.
#
# The testing repositories are disabled by default. To enable, uncomment the
# repo name header and Include lines. You can add preferred servers immediately
# after the header, and they will be used before the default mirrors.
#[kde-unstable]
#Include = /etc/pacman.d/mirrorlist
[core]
SigLevel = PackageRequired
Include = /etc/pacman.d/mirrorlist
[extra]
SigLevel = PackageRequired
Include = /etc/pacman.d/mirrorlist
[community]
SigLevel = PackageRequired
Include = /etc/pacman.d/mirrorlist
# If you want to run 32 bit applications on your x86_64 system,
# enable the multilib repositories as required here.
[multilib]
SigLevel = PackageRequired
Include = /etc/pacman.d/mirrorlist
# An example of a custom package repository. See the pacman manpage for
# tips on creating your own repositories.
#[custom]
#SigLevel = Optional TrustAll
#Server = file:///home/custompkgs