Category: Uncategorized
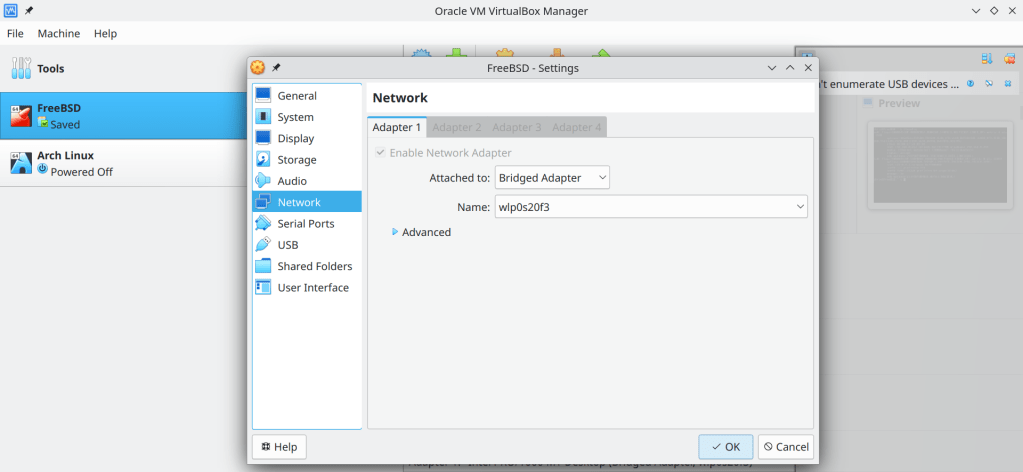
-
- Enable Bridged Adapter
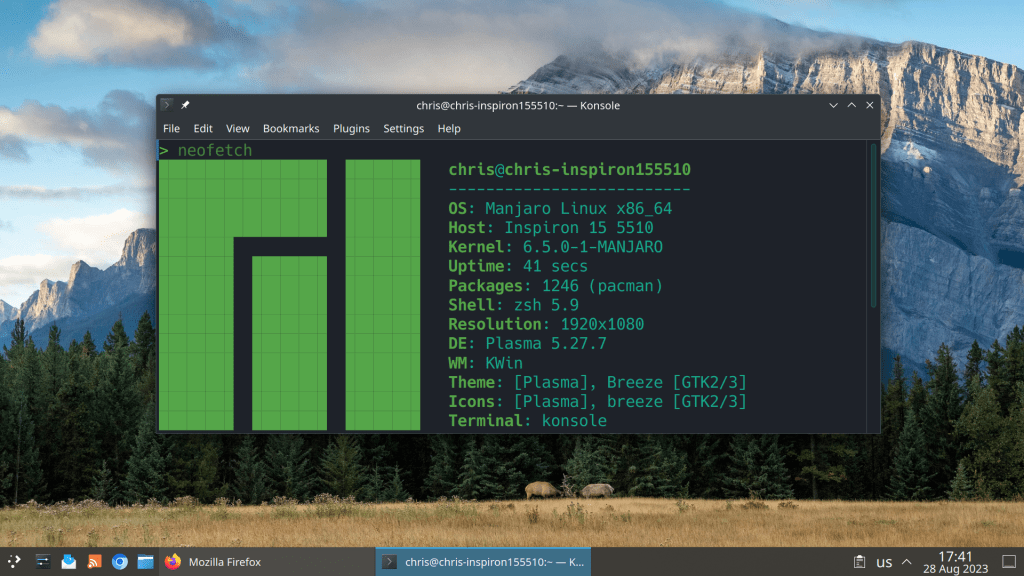
- find the ip adress of the virtual machine using the ifconfig command (in this case 192.168.0.212)
- execute ssh username@ip_adress_of_virtual_machine (in this case ssh chris@192.169.0.212, root@ip_adress does not work for safety reasons!)


-
Visited 452 days, 100 of which consecutive !

-
“In 2017, the kernel jumped from two years of support to six. Now, six years later, it turns out that’s a lot of work. Linux Weekly News executive editor Jonathan Corbet announced the Linux kernel will return to two years of LTS support.
The plan to cut back down to two years isn’t instant.”
According to the article the currently LTS maintained kernels are 6 🙂
-
After more than a decade of active development

-
The problem:

The solution:
sudo rm /var/lib/pacman/db.lck removes the lock of the package database that pacman created when a package is about to get altered. This mechanism prevents a different instance of pacman to perform simultaneous changes but the lock can sometimes remain stale

More about pacman troubleshooting: https://wiki.archlinux.org/title/Pacman#Troubleshooting
-
2 of the most common commands that I use all the time is sudo pacman -Syu for updating packages and sudo pacman -Scc for clearing the package cache
Setting aliases saves a lot of time 🙂
#Aliasesalias update="sudo pacman -Syu && yay -Syu"alias clearcache="sudo pacman -Scc && yay -Scc"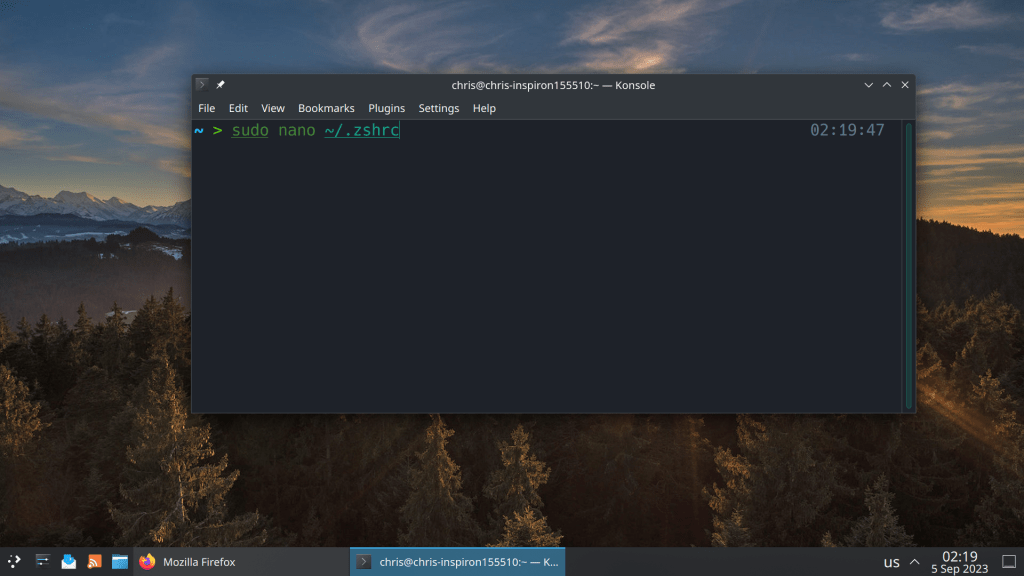
# Enable Powerlevel10k instant prompt. Should stay close to the top of ~/.zshrc. # Initialization code that may require console input (password prompts, [y/n] # confirmations, etc.) must go above this block; everything else may go below. if [[ -r "${XDG_CACHE_HOME:-$HOME/.cache}/p10k-instant-prompt-${(%):-%n}.zsh" ]]; then source "${XDG_CACHE_HOME:-$HOME/.cache}/p10k-instant-prompt-${(%):-%n}.zsh" fi # Use powerline USE_POWERLINE="true" # Source manjaro-zsh-configuration if [[ -e /usr/share/zsh/manjaro-zsh-config ]]; then source /usr/share/zsh/manjaro-zsh-config fi # Use manjaro zsh prompt if [[ -e /usr/share/zsh/manjaro-zsh-prompt ]]; then source /usr/share/zsh/manjaro-zsh-prompt fi # To customize prompt, run `p10k configure` or edit ~/.p10k.zsh. [[ ! -f ~/.p10k.zsh ]] || source ~/.p10k.zsh #Aliases alias update="sudo pacman -Syu && yay -Syu" alias clearcache="sudo pacman -Scc && yay -Scc" -
Pacman is the default package manager of Arch Linux and Arch Linux based distributions. It is considered as the most robust binary package manager along with Portage of Gentoo, a powerful source code package manager.
One of the most important modifications of my setup is the number of parallel downloads and kde-unstable repository
# # /etc/pacman.conf # # See the pacman.conf(5) manpage for option and repository directives # # GENERAL OPTIONS # [options] # The following paths are commented out with their default values listed. # If you wish to use different paths, uncomment and update the paths. #RootDir = / #DBPath = /var/lib/pacman/ CacheDir = /var/cache/pacman/pkg/ #LogFile = /var/log/pacman.log #GPGDir = /etc/pacman.d/gnupg/ #HookDir = /etc/pacman.d/hooks/ HoldPkg = pacman glibc manjaro-system # If upgrades are available for these packages they will be asked for first SyncFirst = manjaro-system archlinux-keyring manjaro-keyring #XferCommand = /usr/bin/curl -L -C - -f -o %o %u #XferCommand = /usr/bin/wget --passive-ftp -c -O %o %u #CleanMethod = KeepInstalled #UseDelta = 0.7 Architecture = auto # Pacman won't upgrade packages listed in IgnorePkg and members of IgnoreGroup #IgnorePkg = #IgnoreGroup = #NoUpgrade = #NoExtract = # Misc options #UseSyslog Color #NoProgressBar # We cannot check disk space from within a chroot environment CheckSpace VerbosePkgLists ParallelDownloads = 5 # By default, pacman accepts packages signed by keys that its local keyring # trusts (see pacman-key and its man page), as well as unsigned packages. SigLevel = Required DatabaseOptional LocalFileSigLevel = Optional #RemoteFileSigLevel = Required # NOTE: You must run `pacman-key --init` before first using pacman; the local # keyring can then be populated with the keys of all official Manjaro Linux # packagers with `pacman-key --populate archlinux manjaro`. # # REPOSITORIES # - can be defined here or included from another file # - pacman will search repositories in the order defined here # - local/custom mirrors can be added here or in separate files # - repositories listed first will take precedence when packages # have identical names, regardless of version number # - URLs will have $repo replaced by the name of the current repo # - URLs will have $arch replaced by the name of the architecture # # Repository entries are of the format: # [repo-name] # Server = ServerName # Include = IncludePath # # The header [repo-name] is crucial - it must be present and # uncommented to enable the repo. # # The testing repositories are disabled by default. To enable, uncomment the # repo name header and Include lines. You can add preferred servers immediately # after the header, and they will be used before the default mirrors. #[kde-unstable] #Include = /etc/pacman.d/mirrorlist [core] SigLevel = PackageRequired Include = /etc/pacman.d/mirrorlist [extra] SigLevel = PackageRequired Include = /etc/pacman.d/mirrorlist [community] SigLevel = PackageRequired Include = /etc/pacman.d/mirrorlist # If you want to run 32 bit applications on your x86_64 system, # enable the multilib repositories as required here. [multilib] SigLevel = PackageRequired Include = /etc/pacman.d/mirrorlist # An example of a custom package repository. See the pacman manpage for # tips on creating your own repositories. #[custom] #SigLevel = Optional TrustAll #Server = file:///home/custompkgs
-
According to Damien Elmes, the author of Anki

-
Ο Linus Torvalds ανακοίνωσε ένα νέο λειτουργικό σύστημα βασισμένο στο Minix. Και τα υπόλοιπα είναι ιστορία 🙂

-
Intel reports up to 50% performance penalties after the microcode update
https://www.phoronix.com/news/New-Linux-Stable-Downfall